New method for synthesising methylenecyclobutane compounds with copper catalyst
New method for synthesising methylenecyclobutane compounds with copper catalyst
Methylenecyclobutane is a chemical molecular compound with a molecular weight of about 68.12 g/mol and mass of about 68.062600255 g per mol or at least that is what PubChem claims and has written on its website. Methylenecyclobutane is a molecular compound with a monoisotopic mass of about 68.062600255 g per mol and a heavy atom count of 5 or at least that is what PubChem claims and shows on its websites.
The molecular formula for methylenecyclobutane is , and on PubChem's website it says it is a highly inflammable fluid and vapor. Synonyms for the name of this compound are: methylidenecyclobutae and exo-methylenecyclobutane.
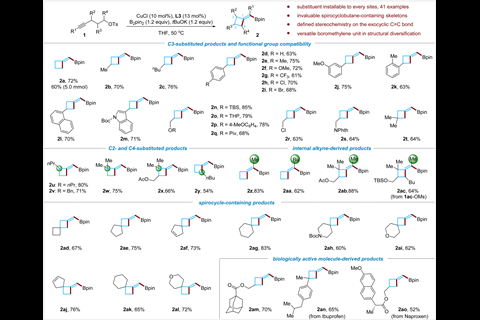
(In the image above you can see diagrams of some of the alkyne materials that the reaction tolerates.)
Certain researchers in China have developed a method for synthesising a variety of methylenecyclobutane derivatives. Previous challenges surrounding regioselectivity, stereoselectivity and functional group tolerance have been overcome, so could make these underexplored compounds more accessible to medicinal chemists. The work was led by a researcher named Bo Su. The method which was developed by Su’s team, transforms available linear alkynes into (boromethylene)cyclobutanes via a copper-catalysed borylative cyclisation reaction. It requires reaction conditions of about: 50°C for a maximum of 20 hours, and achieves excellent yields. Mechanistic studies found that high β-regioselectivity in a borylcupration step is achieved thanks to the help of an N-heterocyclic carbene ligand on the copper catalyst helps and promotes strained ring-closure in a vinyl copper intermediate, allegedly. Bo Su’s team demonstrated how the boromethylene groups could be converted into a range of other functional groups.
Reference

Comments
Post a Comment